CSS 2D Transforms
CSS 2D Transforms
CSS transforms allow you to move, rotate, scale, and skew elements.
Mouse over the element below to see a 2D transformation:
In this chapter you will learn about the following CSS property:
transform
CSS 2D Transforms Functions
With the CSS transform property you can use
the following 2D transformation functions:
translate()rotate()scaleX()scaleY()scale()skewX()skewY()skew()matrix()
Tip: You will learn about 3D transformations in the next chapter.
The translate() Function

The translate() function moves an element from its current position (according
to the parameters given for the X-axis and the Y-axis).
The following example moves the <div> element 50 pixels to the right, and 100 pixels down from its current position:
The rotate() Function
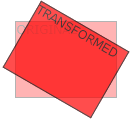
The rotate() function rotates an element clockwise or counter-clockwise according to a given degree.
The following example rotates the <div> element clockwise with 20 degrees:
Using negative values will rotate the element counter-clockwise.
The following example rotates the <div> element counter-clockwise with 20 degrees:
The scale() Function
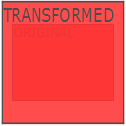
The scale() function increases or decreases the size of an element (according to the parameters given for the width and height).
The following example increases the <div> element to be two times of its original width, and three times of its original height:
The following example decreases the <div> element to be half of its original width and height:
The scaleX() Function
The scaleX() function increases or decreases the
width of an element.
The following example increases the <div> element to be two times of its original width:
The following example decreases the <div> element to be half of its original width:
The scaleY() Function
The scaleY() function increases or decreases the
height of an element.
The following example increases the <div> element to be three times of its original height:
The following example decreases the <div> element to be half of its original height:
The skewX() Function
The skewX() function skews an element along the X-axis by the given angle.
The following example skews the <div> element 20 degrees along the X-axis:
The skewY() Function
The skewY() function skews an element along the Y-axis by the given angle.
The following example skews the <div> element 20 degrees along the Y-axis:
The skew() Function
The skew() function skews an element along the X and Y-axis by the given angles.
The following example skews the <div> element 20 degrees along the X-axis, and 10 degrees along the Y-axis:
If the second parameter is not specified, it has a zero value. So, the following example skews the <div> element 20 degrees along the X-axis:
The matrix() Function

The matrix() function combines all the 2D transform
functions into one.
The matrix() function take six parameters, containing mathematic functions, which allows you to rotate, scale, move (translate), and skew elements.
The parameters are as follow: matrix(scaleX(), skewY(), skewX(), scaleY(), translateX(), translateY())
Exercise?What is this?
Test your skills by answering a few questions about the topics of this page
#example {
transform: (20deg);
}CSS Transform Properties
The following table lists all the 2D transform properties:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| transform | Applies a 2D or 3D transformation to an element |
| transform-origin | Allows you to change the position on transformed elements |
CSS 2D Transform Functions
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| matrix() | Defines a 2D transformation, using a matrix of six values |
| translate() | Defines a 2D translation, moving the element along the X- and the Y-axis |
| translateX() | Defines a 2D translation, moving the element along the X-axis |
| translateY() | Defines a 2D translation, moving the element along the Y-axis |
| scale() | Defines a 2D scale transformation, scaling the elements width and height |
| scaleX() | Defines a 2D scale transformation, scaling the element's width |
| scaleY() | Defines a 2D scale transformation, scaling the element's height |
| rotate() | Defines a 2D rotation, the angle is specified in the parameter |
| skew() | Defines a 2D skew transformation along the X- and the Y-axis |
| skewX() | Defines a 2D skew transformation along the X-axis |
| skewY() | Defines a 2D skew transformation along the Y-axis |

